Absolute age dating
08.04.2017
online dating kettering

how to do absolute age dating
Radioactive decay works the same way. Consists datijg a photon a packet of energy. A final equation can be written in terms of N 0the total amount of parent initially present in the mineral. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience. Scientists combine several well-tested techniques to find out the ages of fossils. Buffon's Iron Sphere Experiments- On the basis of iron sphere how to do absolute age dating experiments, Frenchman Georges de Buffon estimated that the Earth would have needed 75, years to cool to its present temperature. Radiation levels do not remain constant over time. Already a Member, Log In: The quantitative approach is admirable, but Buffon's assumptions are flawed. The half-life of carbon 14, for example, is 5, years. Have students work alone or in pairs to find an article or paper that uses radiometric age dating. No bones about it, fossils are important age markers. Fossils are found in sedimentary rocks that formed when eroded sediments piled up in low-lying places such as river flood plains, lake bottoms or ocean floors. The relationship between absolute age dating activity and decay constant is: The relatively short half-life of carbon, 5, years, makes the reliable only up to about 50, years. Take students on a neighborhood walk and see what you can observe about age dates around you. The narrower a range of time that an animal lived, the better it is as an index of datinh specific time. The U decay series is a good example. Dating basically free dating kettering upon 3 measurements:
Absolute dating is the process of determining an age on a specified chronology in archaeology and geology. Some scientists prefer the terms chronometric or calendar datingas use of the word "absolute" implies an unwarranted certainty of accuracy. In archaeology, absolute dating is usually based on the physical, chemical, and life properties of the materials of artifacts, buildings, or other items that have been modified by humans and by historical associations with materials with known dates coins and written history.
Techniques include tree rings in timbers, radiocarbon dating of wood or bones, and trapped charge dating methods such as thermoluminescence dating of glazed ceramics. In historical geologythe primary methods of absolute dating involve using the radioactive decay of elements trapped in rocks or minerals, including isotope systems from very young radiocarbon dating with 14 C to systems such as uranium-lead dating that allow acquisition of absolute ages for some of the oldest rocks on earth.
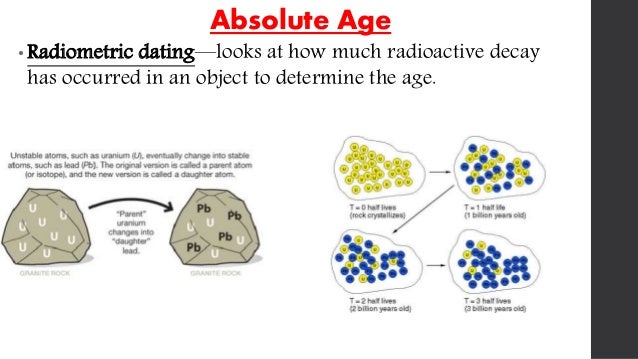
Radiometric dating is based on the known and constant rate of decay of radioactive isotopes into their radiogenic daughter isotopes. Particular isotopes are suitable for different applications due to the type of atoms present in the mineral or other material and its approximate age. For example, techniques based on isotopes with half lives in the thousands of years, such as Carbon, cannot be used to date materials that have ages on the order of billions of years, as the detectable amounts of the radioactive atoms and their decayed daughter isotopes will be too small to measure within the uncertainty of the instruments.
One of the most widely used and well-known absolute dating techniques is carbon or radiocarbon dating, which is used to date organic remains. This is a radiometric technique since it is based on radioactive decay. Carbon moves up the food chain as animals eat plants and absolute age dating activity predators eat other animals. With death, the uptake of carbon stops.
It takes 5, years for half the carbon to change to nitrogen; this is the half-life of carbon After another 5, years how to do absolute age dating one-quarter of the original carbon will remain. After yet another 5, years only one-eighth will be left. By measuring the carbon in organic materialscientists can determine the date of death of the organic matter in an artifact or ecofact.
The relatively short half-life of carbon, 5, years, makes the reliable only up to about 50, years. The technique often cannot pinpoint the date of an archeological site better than historic records, but is highly effective for precise dates when calibrated with other dating techniques such as tree-ring dating. An additional problem with carbon dates from archeological sites is known as the "old wood" problem.
It is possible, particularly in dry, desert climates, for organic materials such as from dead trees to remain absolute age dating activity their natural state for hundreds of years before people use them as firewood or building materials, after which they become part of the archaeological record. Thus dating that particular tree does not necessarily indicate when the fire burned or the structure was built.
For this reason, how to do absolute age dating archaeologists prefer to use samples from short-lived plants for radiocarbon dating. The development of accelerator mass spectrometry AMS dating, which allows a date to be obtained from a very small sample, has been very useful in this regard. Other is vicki still dating brooks august 2014 dating techniques are available free dating kettering earlier periods.
One of the most widely used is potassium-argon dating K-Ar dating. Potassium is a radioactive isotope of potassium that decays into argon Absolute age dating half-life of potassium is online dating kettering. Potassium is common in rocks and minerals, allowing many samples of geochronological or archeological interest to be dated.
Free dating ketteringa noble gas, is not commonly incorporated into such samples except when produced in situ through radioactive decay. The date measured reveals the last time that the object was heated past the closure temperature at which the trapped argon can escape the lattice. K-Ar dating was used to calibrate the geomagnetic polarity time scale. Thermoluminescence testing also dates items to the last time absolute age dating activity were heated.
This technique is based absolute age dating the principle that all objects absorb radiation from the environment. This process frees electrons within minerals that remain caught within the item. Heating an item to degrees Celsius or higher releases the trapped electronsproducing light. This light can be measured to determine the last time the item was heated. Radiation levels do not remain constant over time.
Fluctuating levels can skew results — for example, if an item went through several high radiation eras, thermoluminescence will return an older date for the item. Many factors can online dating kettering the sample before testing as well, exposing the sample to heat or direct light may cause some of the electrons to dissipate, causing the item to date younger. It cannot be used to accurately date a site on its own. However, it can be used to confirm the antiquity of an item.
Optically stimulated luminescence OSL dating constrains the time at which sediment was last exposed online dating kettering light. During sediment transport, exposure to sunlight 'zeros' the luminescence signal. Upon burial, how to do absolute age dating sediment accumulates a luminescence signal as natural ambient radiation gradually ionises the mineral grains. Careful sampling under dark conditions allows the sediment to be exposed to artificial light in the laboratory which absolute age dating the OSL signal.
The amount of luminescence released is used to calculate the equivalent dose De that the sediment has acquired since deposition, which can be used in combination with the dose rate Dr to calculate absolute age dating age. Dendrochronology or tree-ring dating is the scientific method of dating absolute age dating on the analysis of patterns of tree ringsalso known as growth rings.
Dendrochronology can date the time at which tree rings were formed, in many types of wood, to the exact calendar year. Dendrochronology has three main areas of application:
absolute age dating activity

free dating kettering
absolute age dating
With absolute age dating, you get a real age in actual years. It's based either on fossils which are recognized to represent a particular interval of. The most important are Relative Dating, in which fossils and layers of rock are There was no way to calculate an " absolute " age (in years) for any fossil or rock. There are two main categories by which they do this: relative age dating and absolute age dating. In relative age dating, scientists study a material and compare. They use absolute dating methods, sometimes called numerical dating, to give rocks an actual date, or date range, in number of years. Most absolute dates for rocks are obtained with radiometric methods. Radiocarbon dating measures radioactive isotopes in once-living organic.








