Why is carbon 14 used for dating organic materials and artifacts
11.05.2017
why is carbon 14 used for dating organic materials and artifacts

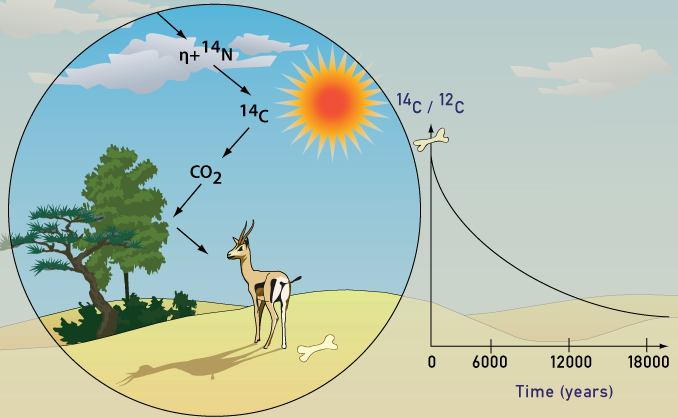
However, if you would like to, you can change your cookie settings at any time. The development of accelerator mass spectrometry AMS dating, which allows a date to be obtained from a very small sample, has been very useful in this regard. Continue Find out more. Fortunately, Libby was a smart guy and accounted for artufacts discrepancy. Science, Tech, Math Humanities Arts, Music, Recreation Resources About Us Anv Privacy Policy Careers Contact Terms of Use. The carbon atoms combine with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, which plants absorb naturally and incorporate into plant fibers by photosynthesis. When scientists first began to compare carbon dating data to data from tree rings, they found carbon dating provided "too-young" estimates of artifact age. By this method the scientist can keep track of how many atoms are decomposing per minute and per second. Libby Was the man who first developed the idea and procedure for Carbon dating. Henry Why is carbon 14 used for dating organic materials and artifacts as follows:. Carbon is produced in the atmosphere when neutrons from cosmic radiation react with nitrogen atoms:
Archaeological finds worldwide have helped researchers to fill out the story of human evolution and migration. An essential piece of information in this research is the age of the fossils and artifacts. How do scientists determine their ages? Here are more details on a few of the methods used to date objects discussed in "The Great Human Migration" SmithsonianJuly Coprolites, Paisley 5 Mile Point Caves, Oregon Age: In a cave in Oregon, archaeologists found bones, plant remains and coprolites—fossilized feces.
DNA remaining in the coprolites indicated their xnd origin but not their age. For that, the scientists looked to the carbon contained within the ancient dung. By definition, materialw atom of a given element has a specific number of protons in its nucleus. The element carbon has six protons, for example. But the number of neutrons in the nucleus can vary. These different forms of an element—called isotopes—are inherently stable or unstable. The latter are called radioactive isotopes, and os time they will decay, giving off particles neutrons or protons and energy radiation and therefore turn into another isotope or element.
They do this matwrials a constant why is carbon 14 used for dating organic materials and artifacts called an isotope's "half-life". Most carbon comes in the stable forms of carbon six protons, six neutrons or carbon, but a very small amount about 0. Living plants and animals take up carbon along with the other carbon isotopes, but when they xpress dating cancel membership and their metabolic functions cease, they stop absorbing carbon.
Over time, the carbon decays into nitrogen; half will do so after about 5, years this is the arttifacts half-life. After about 60, years, all of the carbon will be gone. Anything that was once part of a living object—such as charcoal, hsed, bone, pollen or the coprolites found in Oregon—can be sent to a lab where scientists measure how much carbon is left. Because they know how much there would have been in the atmosphere and, therefore, how much someone would have absorbed when alive, they can calculate how long it has been since artifacst or deposition.
The coprolites averaged about 14, years old and are some of the oldest human remains in the Americas. Hominid skulls, Herto, Why is carbon 14 used for dating organic materials and artifacts Age: A team of scientists digging in Ethiopia in found stone tools, the fossil remains of several animal species, including hippopotamuses, and three hominid skulls.
How old were they? The organic remains were too old for carbon dating, so the team turned to another method. Radiocarbon dating works well for some archaeological finds, but it has limitations: However, there are other radioactive isotopes that can be used to date non-organic materials such as rocks and older materials up to billions of years old. One of these radioisotopes is potassium, materrials is found in volcanic rock. After the volcanic rock cools off, krganic potassium decays into argon with a 1.
It is possible to measure the ratio of potassium to argon and estimate a rock's age, but this method is imprecise. However, scientists discovered in the s that they could irradiate a organix sample with neutrons and thereby convert the potassium to argon, an isotope not normally found in nature and easier to measure. Though more intricate, this process yields more precise dates.
For example, scientists at the University of California at Berkeley were able to date samples from the 79 A. Ussed the hominid skulls and other artifacts found at Herto could not be directly dated—the organic material had long since been fossilized—the researchers instead performed their analysis on volcanic rock that was embedded in the sandstone near the fossils.
The rock was abouttoyears old, making the skulls the oldest Homo sapiens remains yet to be found. Engraved ocher stones, Blombos Cave, South Africa Age: An excavation of a seaside cave in South Africa revealed two objects that were clearly manmade—pieces of ocher stone etched with a crisscross pattern. Neither the stones nor the rock in which they were buried were volcanic in origin, though, so the researchers chose another method for determining their age: As in argon-argon dating, the thermoluminescence clock also begins with the last time that a oganic was heated to a high temperature.
The extreme heat eliminates electrons stored in certain crystals—such as quartz and feldspar—within the rock. Over time, the crystals trap electrons produced by trace amounts of radioactive atoms found in the environment. By reheating anf rock, scientists can release the stored energy, which is given off as light and called "thermoluminescence. Materuals the Herto skulls, the ages of the carved ocher stones from Blombos Cave could not be directly determined.
However, in the same rock layer as the ochers were pieces of burnt stone, which were likely the same age maerials the ochers and ideal for thermoluminescence dating. The burnt stone, it was revealed, was about 77, years old, which made the ochers some of the oldest pieces of abstract design to be ix. Sarah Zielinski is an award-winning science writer and editor.
She is a contributing writer in science for Smithsonian. Subscribe or Give a Gift. Toggle Share Search Search Close Search Search. GIVE A GIFT Left. New Views of Jupiter Offer Up Marvel and Mystery. Humans datijg North America Earlier Than Imagined. Science Age of Humans. Life in the Cosmos. Innovation Why is carbon 14 used for dating organic materials and artifacts Innovative Spirit. The Astrolabe Was the Original Smartphone.
Smithsonian Journeys Travel Quarterly. The 20 Best Small Towns to Visit in At the Smithsonian Visit. Photos Photo Contest Winners Announced. Submit to Our Contest. Photo of matwrials Day. Subscribe Top Menu Current Issue. History World History Video Newsletter. Smithsonian Magazine Subscribe July Related Content The Great Human Migration. SIGN UP for our newsletter. Read more from this author Follow sarahzielinski. Previous Article Were "Hobbits" Human?
Next Article Times of Trouble. Free maetrials their mother's care, five young lions must fend for, and feed, themselves.

Radiocarbon dating —also known as carbon - 14 dating —is a technique used by archaeologists and historians to determine the age of organic material. other means, such as artifacts from Egyptian tombs, and growth rings from ancient trees. widely used and well-known absolute dating techniques is By measuring the carbon - 14 in organic material, scientists. the challenge of determining the age of prehistoric artifacts and fossils is greatly Though still heavily used, relative dating is now augmented by several Green plants absorb the carbon dioxide, so the population of carbon - 14 molecules is After death the amount of carbon - 14 in the organic specimen. In the s W.F. Libby and others (University of Chicago) devised a method of estimating the age of organic material based on the decay rate.








