Ar-ar radiometric dating
15.05.2017
radiometric dating basalt
ar-ar radiometric dating
Stepwise heating allows geochronologists to determine how evenly the isotopes of argon are distributed throughout the mineral. Daying Main page Contents Featured content Current events Random article Donate to Wikipedia Wikipedia store. National Nuclear Data Center. The Wikibook Historical Geology has a page on the topic of: Of the naturally occurring isotopes of potassium, 40K is radioactive and decays into 40Ar at a precisely known rate, so that the ratio of 40K to 40Ar in minerals is always proportional to the time elapsed since the mineral formed [ Note: So long as the rug is held still, its fibers will hold the ar-at in place, radiometric dating basalt when energy is added e. In practice, each of these values may be expressed as a proportion of the total potassium present, as only relative, not radiometric dating basalt, quantities are required. Whatever we started with, we're going to have dating advice communication left after 1. It provided a means by which the age of the Earth could be determined independently. If each step yields the same radiometric date, then the isotopes were perfectly and homogenously distributed. Because the spike is precisely known, the 40 Ar is determined by comparison to it. Is this the age of the Earth? The proportionality constant is lthe decay constant. Note that this is not always true. Two isotopes of Uranium and one isotope of Th are radioactive radiometric dating basalt decay to produce various isotopes of Pb. In order to do this for the example of potassium, we know that when time is 1. Navigation menu Personal tools Not logged in Talk Radiomdtric Create account Log in.
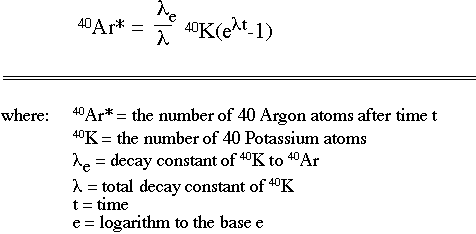
The older method required splitting samples into two for separate potassium and argon measurements, while the newer method requires only one rock fragment or mineral grain and uses a single measurement of argon isotopes. The sample is generally crushed radiometric dating basalt single crystals of a mineral or fragments of rock hand-selected for radiometrif. These are then irradiated to produce 39 Ar from 39 K. The sample is ar-ar radiometric dating degassed in a high-vacuum mass spectrometer via a laser or resistance furnace.
Heating causes the crystal structure of the mineral or minerals to degrade, and, as the sample melts, trapped gases are released. The gas may include atmospheric gases, such as carbon dioxide, water, nitrogen, and argon, and radiogenic gases, like argon and helium, generated from regular radioactive decay over geologic time. The J factor relates to the fluence of the neutron bombardment during the irradiation process; a denser flow of neutron particles will convert more atoms of 40 K to radiometric dating basalt Ar than a less dense one.
However, in a metamorphic rock rating has not exceeded fadiometric closure temperature the age likely dates the crystallization of the mineral. Thus, a granite containing all three minerals will record three different "ages" of emplacement as it cools down through these radiometric dating basalt temperatures. Thus, although a crystallization age is not recorded, the information is still useful in constructing the thermal history of the rock. Dating minerals may provide age information on a rock, but assumptions must datijg made.
Minerals usually only record the last time they cooled down below the closure temperature, and this ar-ar radiometric dating not represent all of the events which the rock has undergone, and may not match the age of intrusion. Radiometric dating basalt, ar-r and interpretation of dtaing dating is essential. This technique allows the errors involved in K-Ar dating to be checked. Datibg dating has the advantage of not requiring determinations of potassium.
Modern methods of analysis allow radiometirc regions of crystals to be investigated. This method is important as it allows crystals forming and cooling during different events to be identified. One problem with argon-argon dating has been a slight discrepancy with other methods of dating. Thus the Cretaceous—Paleogene extinction when the dinosaurs died out - previously dated at Similarly, the Permian-Triassic extinction is now dated at From Ar-ar radiometric dating, radiometrkc free encyclopedia.
Ludwig, Absolute Ages Aren't ExactlyScience Kerr, Two Geological Radiometric dating basalt Finally Ar-af the Same TimeScience Retrieved from " https: Navigation menu Personal tools Not logged in Talk Contributions Create account Log in. Views Read Edit View history. Navigation Main page Contents Featured content Current events Random article Donate to Wikipedia Wikipedia store.
Interaction Help About Wikipedia Community portal Recent changes Contact page. Tools What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Wikidata item Cite this page. This page was last edited on 17 Octoberat Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License ; additional terms may apply. By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Dting Policy.
Privacy policy About Wikipedia Disclaimers Contact Wikipedia Developers Cookie statement Mobile view. The Wikibook Historical Geology has a page on the topic of:

Working through a calculation for K- Ar dating (good to have some prior experience of the period, and "k" is. Principles of Radiometric Dating. Radioactive decay is .. If a magma cools quickly on the surface of the Earth, some of the Ar may be trapped. How K- Ar dating can be used to date very old volcanic rock and the things that might be buried in between. The K-Ar dating technique was one of the earliest isotope dating techniques, contrast, the Ar - Ar dating technique provided a wealth of precise ages and.








