Surface exposure dating with cosmogenic nuclides
03.06.2017
surface exposure dating with cosmogenic nuclides
Click to expose these in surface exposure dating with cosmogenic nuclides workspace D. Glacial geologists are often interested in dating the maximum extents of glaciers or rates of recession, and so will look for boulders deposited on moraines. Using cosmogenic nuclides in glacial geology Sampling strategies cosmogenic nuclide dating Difficulties in cosmogenic nuclide dating Calculating an exposure age Further Reading References Comments. The apparent age gap has been subject to discussions from both, methodological and geomorphological viewpoints. Opens the author workspace Opens the author workspace a. Articles by Sharma, M. Relict rock glaciers provide information on past discontinuous permafrost and former mean annual air temperatures. Spallation reactions occur in minerals in the rocks upon bombardment by cosmic rays. Issue Purchase 30 days access for USD Notably, at sites just inside of the LIA extent, which do exhibit fresh glacial polish, concordant ages suggest that subglacial erosion there was minimal. Skip to content Kelsey Winsor. Interaction Help About Wikipedia Community portal Recent changes Contact page. Cosmogenic nuclide dating is cksmogenic over short cosmovenic long timescales 1,, yearsdepending on which isotope you are dating. Privacy policy About Wikipedia Disclaimers Contact Wikipedia Surface exposure dating with cosmogenic nuclides Cookie statement Mobile view. By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.

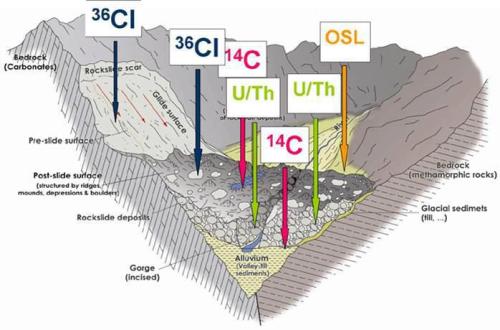
Radiocarbon dating is abundantly used and offers very high precision dates, but we often want to date an event that is either too far in the past, or without the right type of organic matter, to be dated by 14 C. If we are particularly interested in the timing of the uncovering of a surface—say, bedrock that had been covered by ice, or sediments that had been revealed by the incision of a stream—we can employ cosmogenic nuclide surface exposure dating to study that uncovering process.
Super high energy particles—mostly protons— are produced by our Sun, supernovae, and probably other extraterrestrial sources. These particles continuously enter the Earth system at incredible rates and are often, but misleadingly, called cosmic rays. Depending on the elements that a particle collides with, it produces different end products. Because 10 Be is only produced by interaction with cosmogenic radiation, measuring the concentration of 10 Be in a sample can allow you to determine how long it has been exposed to cosmic radiation.
Skip to content Kelsey Winsor. Surface Exposure Dating Why surface exposure dating with cosmogenic nuclides cosmogenic nuclide exposure dating? How does 10 Be exposure dating work? Contact Info Department of Environmental, Earth surface exposure dating with cosmogenic nuclides Atmospheric Sciences 1 University Ave University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell, MA kelsey.
Create a free website or blog at WordPress.

The concentration of cosmogenic nuclides in rocks is used by geomorphologists to gain knowledge on the age of landforms such as moraines or landslides. Terrestrial cosmogenic nuclide surface exposure dating of moraine boulders and alluvial fan sediments define the timing of five glacial advances over at least. In situ cosmogenic nuclides have become a powerful means to determine surface exposure ages of boulders on moraines and other landforms that are. Cosmogenic exposure dating Some cosmic ray particles reach the surface of the earth and contribute to the natural background radiation environment. An age determined by measurement of the amount of each nuclide would be an.








